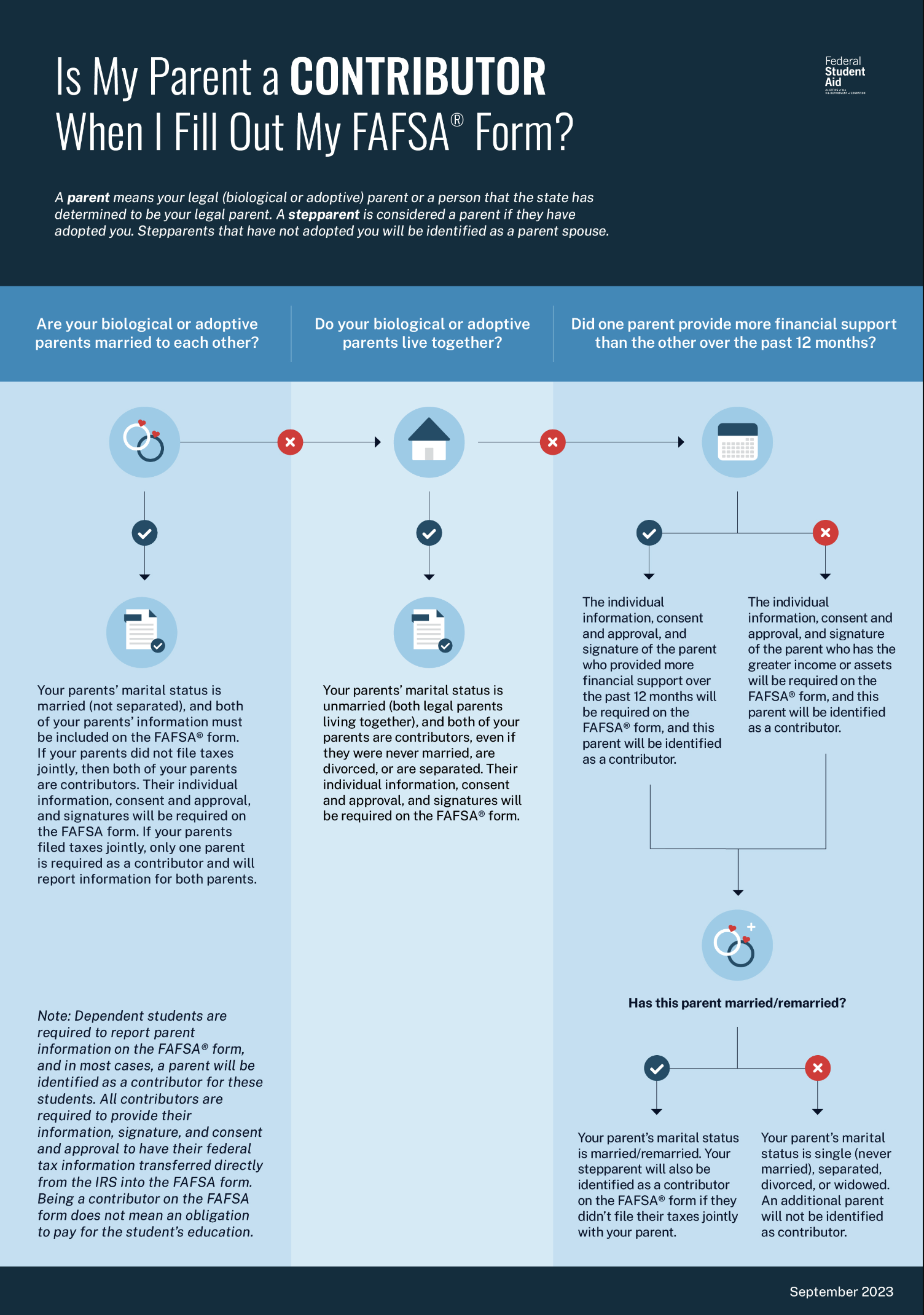
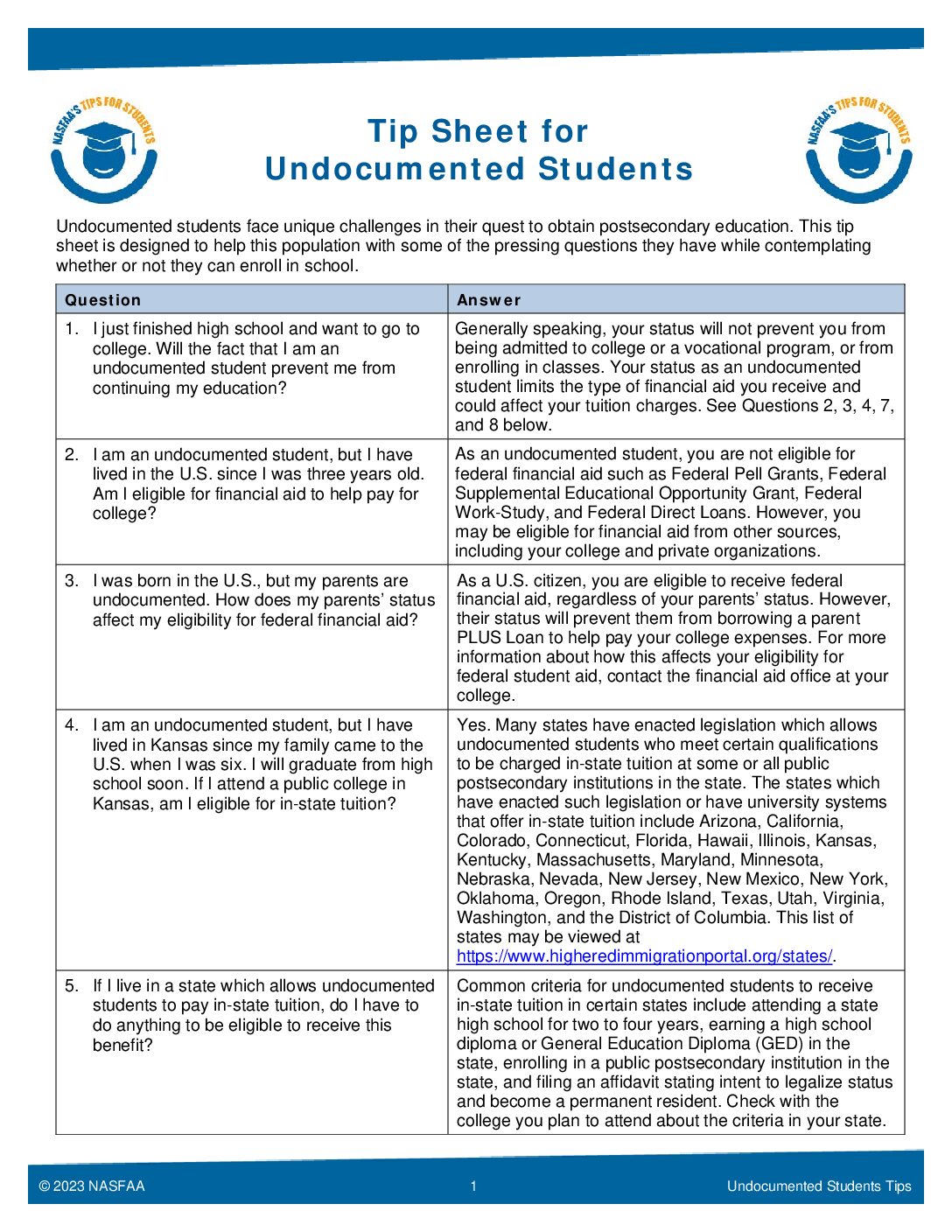
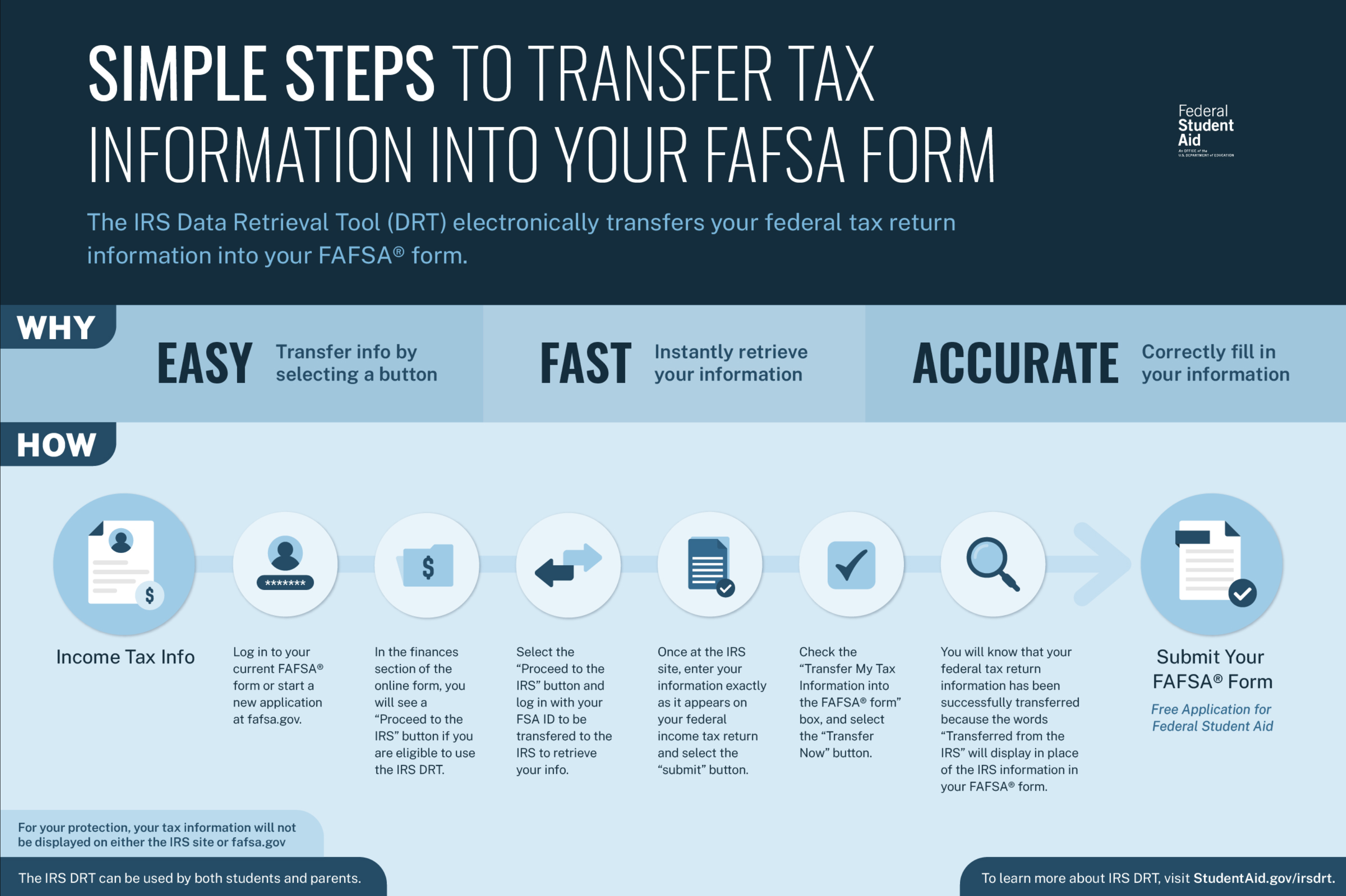
The 2024-2025 FAFSA Form launching in December 2023 will reflect six key changes. According to studentaid.gov, the FAFSA Simplification Act represents a significant overhaul of the processes and systems used to award federal student aid starting with the 2024–25 award year. This includes the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA®) form, need analysis, and many policies and procedures for schools that participate in federal student aid programs. The law will also affect every state that uses FAFSA data to award state grant aid and every school that participates in the federal student aid programs.
Federal Student Aid provides more than $125 billion in federal grants, work-study, and loans for students attending career schools, community colleges, and colleges or universities. There are several programs for students to take advantage of as they prepare to advance their education:
- Grants – a grant is a form of financial aid that doesn’t have to be repaid (unless, for example, you withdraw from school and owe a refund, or you receive a TEACH Grant and don’t complete your service obligation). A variety of federal grants are available, including Pell Grants, Federal Supplemental Educational Opportunity Grants, Teacher Education Assistance for College and Higher Education (TEACH) Grants, and Iraq and Afghanistan Service Grants.
- Scholarships – many nonprofit and private organizations offer scholarships to help students pay for college or career school. This type of free money, which is sometimes based on academic merit, talent, or a particular area of study, can make a real difference in helping you manage your education expenses.
- Work-Study Jobs – the Federal Work-Study Program allows you to earn money to pay for school by working part-time. You’ll earn at least the current federal minimum wage. However, you may earn more depending on the type of work you do and the skills required for the position. Your total work-study award depends on when you apply, your level of financial need, and your school’s funding level.
- Loans – a loan is money you borrow and must pay back with interest. If you apply for financial aid, you may be offered loans as part of your school’s financial aid offer. When you receive a student loan, you are borrowing money to attend a college or career school. You must repay the loan as well as interest that accrues. It is important to understand your repayment options so you can successfully repay your loan.
- Aid for Military Families – there are special aid programs or additional aid eligibility for serving in the military or for being the spouse or child of a veteran.
- Aid for International Study – federal student aid may be available for studying at a school outside the United States, whether you’re studying abroad or getting your degree from an international school.
You can apply for federal student aid—grants, work-study, and loans—using the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA®) form. You can also learn more about federal financial aid by reviewing the resources below. Also make sure to check out Career Pathways to see what level of eduction you will need to meet your goals.